Study Reveals Stark Disparities in Breast Cancer Mortality Rates Across US Counties
A groundbreaking study has unveiled a troubling disparity in breast cancer mortality rates among women residing in different counties within the same state. This research, conducted in Virginia, analyzed federal data encompassing over 2,000 counties, shedding light on the varying degrees of influence exerted by major risk factors such as obesity and a history of smoking on breast cancer mortality.
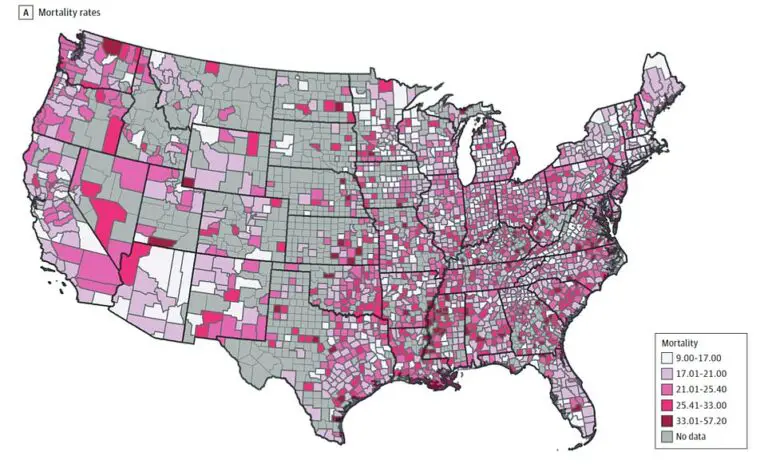
The results are eye-opening, demonstrating that where individuals live can significantly affect their risk of breast cancer mortality. In some counties, the odds of succumbing to breast cancer are six times higher than in neighboring ones. For example, Lamar County, Alabama, reports a staggering one in 33 women losing their lives to breast cancer, while nearby Cullman sees a rate as high as one in nine.
These findings underscore the need for more comprehensive and geographically targeted interventions to foster healthier communities.
The study not only reveals disparities between states but also within individual counties. Alabama serves as a clear example, with significant variations in mortality rates between northern and southern regions. It’s not an isolated case; other states, like North Carolina and Utah, exhibit striking discrepancies in breast cancer mortality rates between adjacent counties.
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women in the United States. However, there’s been a remarkable 43 percent reduction in death rates between 1989 and 2020, thanks to improved awareness, better screening, and innovative treatments.
Various factors contribute to these disparities. Obesity proves influential across all counties, with the southeastern U.S. experiencing slightly higher impact rates. In the eastern states, access to mammograms plays a significant role in mortality rates.
Access to nutritious food demonstrates varying impacts across regions. Southern and eastern states show a stronger association between food access and breast cancer death rates. Additionally, access to healthcare services, including preventative measures like mammograms, has a universal impact on reducing breast cancer deaths.
The study relied on statistical analysis methods, Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) and Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression (MGWR), to explore county-level data. Coefficients were used to measure the strength of relationships between variables. Higher coefficients indicate stronger relationships.
Both models revealed uniform impacts of mammogram uptake and obesity across most counties, particularly spanning from North Carolina to Florida and eastern Oklahoma to Texas. Mammogram access showed even greater influence in eastern seaboard counties, from Maine to North Carolina.
This research underscores the importance of targeted interventions and continued efforts to reduce breast cancer mortality rates, ultimately saving more lives. The study’s findings were published in the journal JAMA Network Open.